Using Relational.OWL Explains how
to use Relational.OWL's own GUI or include it into another
application.
This
is a preliminary implementation of Relational.OWL, realizing most of
the basic functionality. It shall give the reader the possibility to
understand the underlying technology and include it into his own
applications. Since this version of the package is still a little
buggy, it comes without any warranty.
Relational.OWL is a Semantic Web-based representation format for
relational data and schema components, which is particularly
appropriate for exchanging items among remote database systems or to
expose relational data on the Semantic Web. OWL, originally created
for the Semantic Web enables us to represent not only the relational
data itself, but also a part of its interpretation, i.e.
knowledge about its format, its origin, its usage, or its original
embedment in specific frameworks.
To describe the schema of a relational database with the techniques
provided by RDF and OWL, we have defined reference OWL classes
centrally, to which any document describing such a database can
refer. The abstract representation of classes like
Table or
Column become a central part of the knowledge representation
process realized within Relational.OWL. Additionally, we have
specified possible relationships among these classes resulting in an
ontology, a relational database can easily be described with. We
call this central representation of abstract schema components and
relationships the
Relational.OWL Ontology.
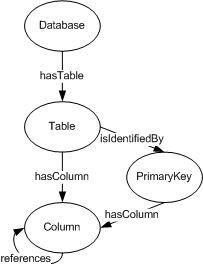 The Relational.OWL Ontology
The Relational.OWL Ontology
Relataional.OWL, the software package presented here, connects to a
relational database using a genuine JDBC-Connection and mediates
between the relational and the semantic worlds. On the one hand, it
converts a database schema automatically into a suitable RDF/OWL
ontology and represents the corresponding data items as its
instances. On the other hand, it processes schema and data
representations and imports them into a suitable database. Please
note, that the data and schema representation files have to be based
no the Relational.OWL Ontology.
Relational.OWL is written in Java, uses JDBC for the database and
the JENA framework for the Semantic Web connectivity. Since the
RDF/OWL representation of the database is vendor-independent, a data
and schema extract of a database from vendor A can easily be
imported into a database from another vendor. Relational.OWL
currently supports MySQL and DB2 databases, but a corresponding
implementations for additional vendors may easily be added.
Required Packages
The following external JAR-Packages, or
equivalent, are required for using Relational.OWL:
- commons-logging.jar
- concurrent.jar
- icu4j.jar
- jakarta-oro-2.0.5.jar
- jdom.jar
- jena.jar
- xercesImpl.jar
- JDBC-Driver, e.g.:
mysql-connector-java-3.1.10-bin.jar
GUI
As soon,
as the main class of the programm
de.hhu.cs.dbs.RelationalOWL is started,
the GUI window appears. The window consits of three tabs:
Import,
Export, and
Config.
The required
connection properties have to be specified within the
Config
tab, where they also may be saved or loaded from a corresponding
property file. After pressing the
Reload button,
Relational.OWL connects to the specified database and is ready to
start an import or export task. Depending on the required
functionality, the user may either switch to the
Import or
Export tabs. The main features of the GUI may then be used
intuitively. Besides the export of a complete database,
Relational.OWL is capable to export data based on an SQL statement.
This statement can be specified in the
Export tab.
Schema Export
Relational.OWL may also be included into
existing Semantic Web applications and does not require the GUI for
its functionality. In the following code snippet, first, a
connection to a relational database is created, then the
corresponding schema is extracted and finally printed through the
standard output stream.
DbManager dbManager = DatabaseManagerFactory.getDbManagerInstance(connection information);
ExportSchemaTask taskES = new ExportSchemaTask(dbManager.getConnection(),driver, database);
taskES.go();
while (!taskES.isDone()){
Thread.sleep(100);
}
OntModel schema=ModelFactory.createOntologyModel(OntModelSpec.OWL_MEM,null);
schema = taskES.getSchemaOntology();
schema.setNsPrefix("dbs","https://www.dbs.cs.uni-duesseldorf.de/RDF/relational.owl#");
RDFWriter utf8Writer = schema.getWriter("RDF/XML-ABBREV");
utf8Writer.setProperty("allowBadURIs","true");
utf8Writer.setProperty("relativeURIs","same-document,relative");
utf8Writer.write(schema, System.out, "");
|
Data Export
After the schema has been exported, the data
instances may be processed. Although a schema file is not strictly
required to extract the data, it is advisable to specify it,
otherwise the data instances could not be linked to the
corresponding schema ontology.
ExportDataTask taskED= new ExportDataTask(dbManager.getConnection(),driver,database,schemaLoc);
taskED.go();
while (!taskED.isDone()){
Thread.sleep(100);
}
OntModel data=taskED.getDataOntology();
RDFWriter utf8DataWriter= data.getWriter("RDF/XML-ABBREV");
utf8DataWriter.setProperty("allowBadURIs","true");
utf8DataWriter.setProperty("relativeURIs","same-document,relative");
utf8DataWriter.write(data, System.out, "");
|
Schema Import
Relational.OWL is not only capable to export
data or schema components of a relational database, but it also
imports formerly exported schemata and data into a corresponding
database. The following snippet shows how to import a schema
ontology into a relational database for creating there a new schema.
String importSchemaPath = pathToSchema;
DatabaseManagerFactory.getDbManagerInstance(connection information);
ImportSchemaTask taskIS = new ImportSchemaTask(dbManager.getConnection(), driver, importSchemaPath);
taskIS.go();
while (!taskIS.isDone()){
Thread.sleep(100);
}
|
Data Import
After having imported the schema of the
relational database, we may now proceed to the data import. It is
quite analogous to the schema import task. Please note, that the
corresponding schema has to be created before a data import task can
be started.
ImportDataTask taskID = new ImportDataTask(dbManager.getConnection(),driver,schemaPath,dataPath);
taskID.go();
while (!taskID.isDone()){
Thread.sleep(100);
}
|
Additional Requirements
If you want to build up an application using the Relational.OWL JAR-File, please note the following information:
- RelationalOWL - A Data and Schema Representation Format Based on OWL; Cristian
Pérez de Laborda and Stefan Conrad;Conceptual Modelling 2005,
Second Asia-Pacific Conference on Conceptual Modelling (APCCM2005);
pp 89-96
- Querying Relational Databases with RDQL;
Cristian Pérez de Laborda and Stefan Conrad; Berliner XML
Tage 2005; pp 161-172
- Semantic Web Activities at the Databases and Information Systems Group Düsseldorf - https://www.dbs.cs.uni-duesseldorf.de/RDF/
- Jena – A Semantic Web Framework for Java - http://jena.sourceforge.net/

